Amerigo Vespucci: The Explorer Who Defined a Continent
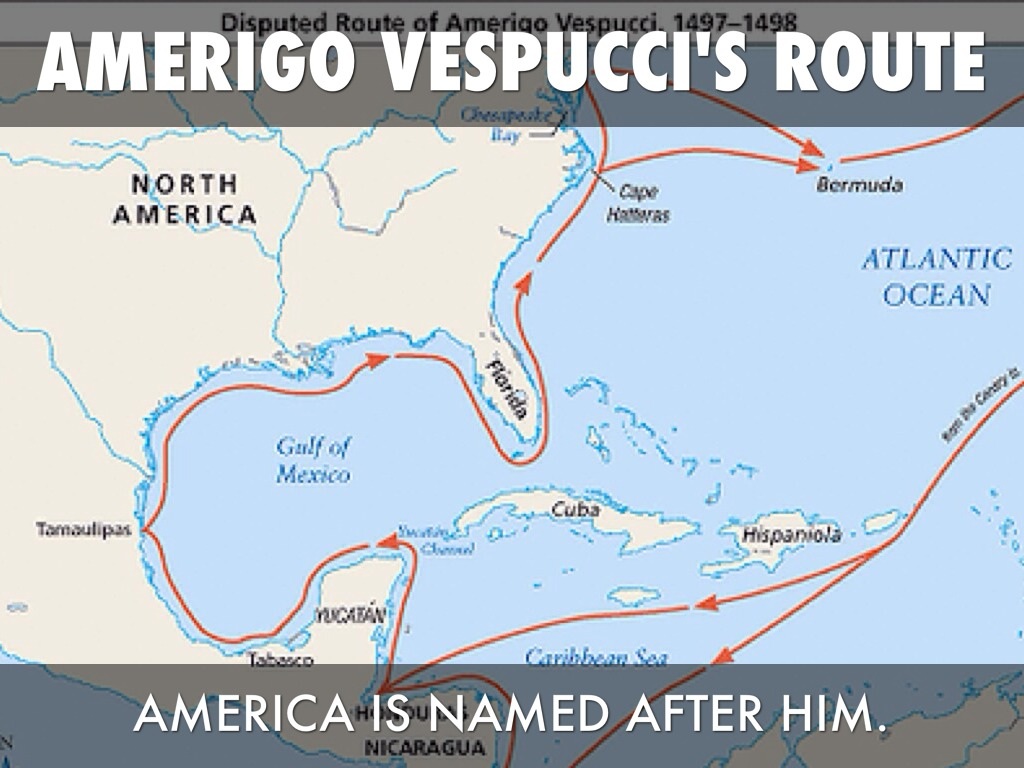
The name Amerigo Vespucci is synonymous with exploration and discovery, yet many people may not fully appreciate the significance of his contributions to our understanding of the New World. Born in Florence, Italy, in 1454, Vespucci played a crucial role in the Age of Exploration, a period marked by Europeans venturing into uncharted territories. His voyages across the Atlantic Ocean not only expanded geographical knowledge but also influenced the naming of the Americas. This article will delve into the life of Amerigo Vespucci, his exploration routes, and his lasting impact on the world.
Quick Info Table: Key Facts about Amerigo Vespucci
| Fact | Details |
|---|---|
| Born | March 9, 1454, Florence, Italy |
| Died | February 22, 1512, Seville, Spain |
| Significant Voyages | 1497, 1499, 1501, 1503 |
| Key Contributions | Mapping parts of South America, naming America |
| Notable Works | "Mundus Novus," "Lettera" |
The Early Years of Vespucci
Background and Education
Amerigo Vespucci came from a family of notable merchants and had a strong educational background. He studied astronomy, navigation, and cartography, which laid the foundation for his future as an explorer. His early career involved working for the Medici family, who were influential patrons of the arts and sciences during the Renaissance. It was through this connection that Vespucci gained access to the maritime world.
Entry into Exploration
In the late 1490s, driven by a desire for adventure and discovery, Vespucci embarked on his first voyage. Unlike many of his contemporaries, he approached exploration with a scientific mindset, aiming to understand the lands he encountered rather than simply claiming them for European powers.
The Exploration Routes of Amerigo Vespucci
The First Voyage: 1497
Vespucci's first voyage took place in 1497, although the details are somewhat unclear. He sailed under the Portuguese flag, exploring the coast of Brazil. During this expedition, he meticulously recorded observations about the flora, fauna, and indigenous cultures he encountered.
The Second Voyage: 1499
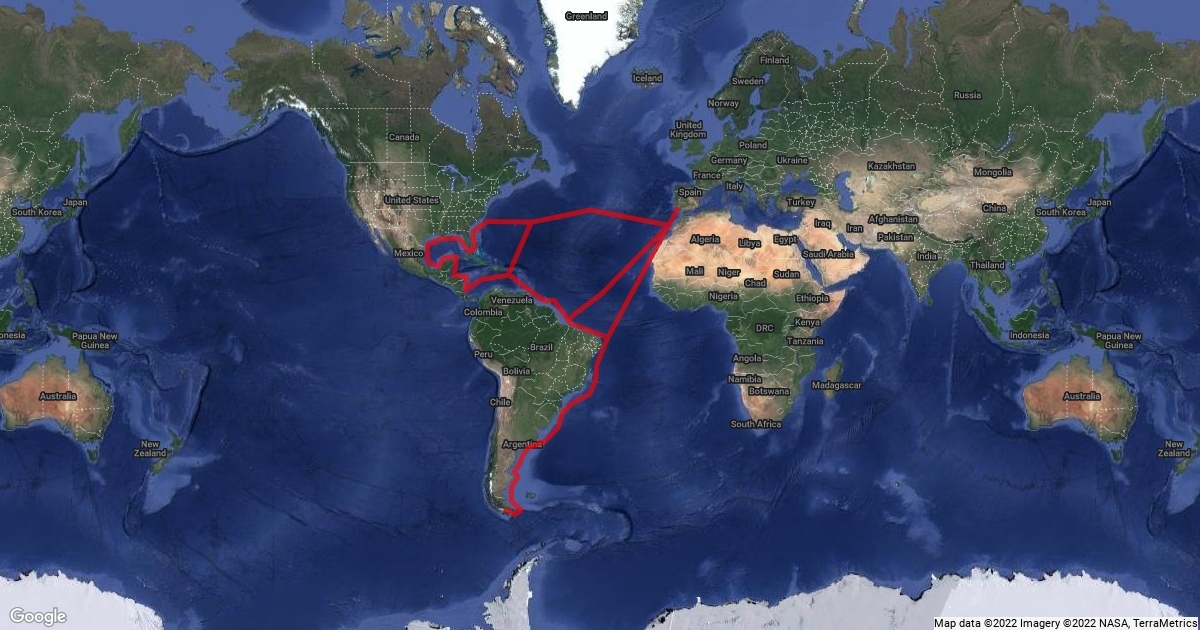
In 1499, Vespucci embarked on a more significant journey, sailing along the northern coast of South America. This voyage brought him to the Orinoco River in present-day Venezuela. His observations during this expedition were crucial in understanding the geography of the region. Vespucci began to formulate the idea that the lands he was exploring were part of a new continent, separate from Asia, which many Europeans believed they had reached.
The Third and Fourth Voyages: 1501-1504
Vespucci's subsequent voyages, particularly those made between 1501 and 1504, were pivotal in mapping the coastlines of South America and parts of Central America. On these journeys, he sailed under the Spanish flag and explored further south, reaching the Rio de la Plata and the Patagonian coast. His detailed accounts laid the groundwork for future maps and navigation routes, and his observations were published in works that captured the imagination of Europe.
Contributions to Geography
New World vs. Old World
One of Vespucci's most significant contributions was his assertion that the lands he explored were part of a "New World." This was a revolutionary idea at the time, challenging the prevailing belief that explorers were reaching the outskirts of Asia. His letters and reports, especially "Mundus Novus," provided compelling evidence of the distinct nature of these territories.
The Naming of America
The impact of Vespucci's explorations extended beyond mapping and documentation. In 1507, the German cartographer Martin Waldseemüller published a world map that labeled the new continent as "America" in honor of Amerigo Vespucci. This decision solidified Vespucci's legacy in history, as the name stuck and became synonymous with the continents of North and South America.
Vespucci's Legacy
Influence on Cartography
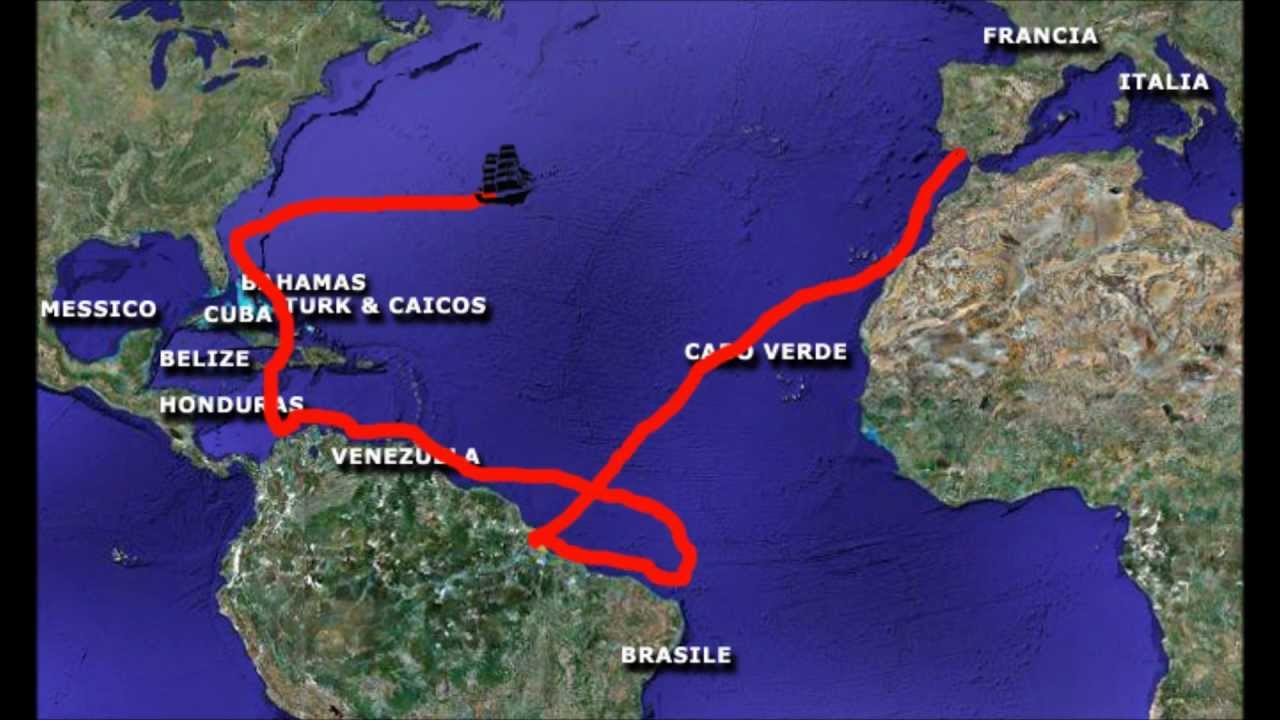
Vespucci’s detailed observations and innovative methods significantly advanced the field of cartography. His emphasis on accurate measurements and the use of celestial navigation techniques helped future explorers and cartographers create more precise maps. His contributions also inspired subsequent generations of explorers, including Ferdinand Magellan and James Cook, who built upon his work to navigate the seas.
Cultural Impact
The cultural impact of Vespucci's voyages cannot be overstated. His writings introduced European audiences to the diverse cultures and peoples of the Americas. By sharing insights about indigenous communities, their customs, and their languages, Vespucci fostered a greater understanding of the New World, paving the way for future interactions between Europeans and Native Americans.
Modern Recognition
Today, Amerigo Vespucci is recognized as one of the key figures in the Age of Exploration. His explorations are commemorated in various ways, including the naming of the continent and numerous monuments dedicated to his legacy. Educational institutions, streets, and geographical features bear his name, ensuring his contributions are not forgotten.
Controversies Surrounding Vespucci
The Debate Over Authenticity
Despite his achievements, Vespucci's legacy is not without controversy. Questions have arisen regarding the authenticity of some of his accounts. Critics argue that he may have exaggerated the discoveries or misrepresented certain aspects of his voyages. However, many historians maintain that Vespucci’s overall contributions to geography and exploration remain significant.
Alternative Perspectives
While Vespucci is often credited with the naming of America, some scholars argue that other explorers, like Christopher Columbus, should also be recognized for their roles in the European discovery of the New World. This debate highlights the complexities of exploration history, where multiple figures contributed to the understanding and mapping of new territories.
Conclusion
In summary, Amerigo Vespucci was a pioneering explorer whose voyages and observations reshaped the understanding of the New World. His meticulous documentation and innovative methodologies not only advanced cartography but also led to the naming of America, a legacy that endures to this day. Although controversies surround his accounts, the overall impact of his contributions remains significant in the annals of exploration history.
As we reflect on the age of exploration, it is essential to recognize the complexity of this period and the individuals who shaped it. Vespucci's journey serves as a reminder of the spirit of inquiry and adventure that drove explorers to seek new horizons, ultimately transforming our world. For those interested in exploration and its consequences, Vespucci's story offers valuable insights and lessons that continue to resonate today.
